 What Is FWCI?
What Is FWCI?
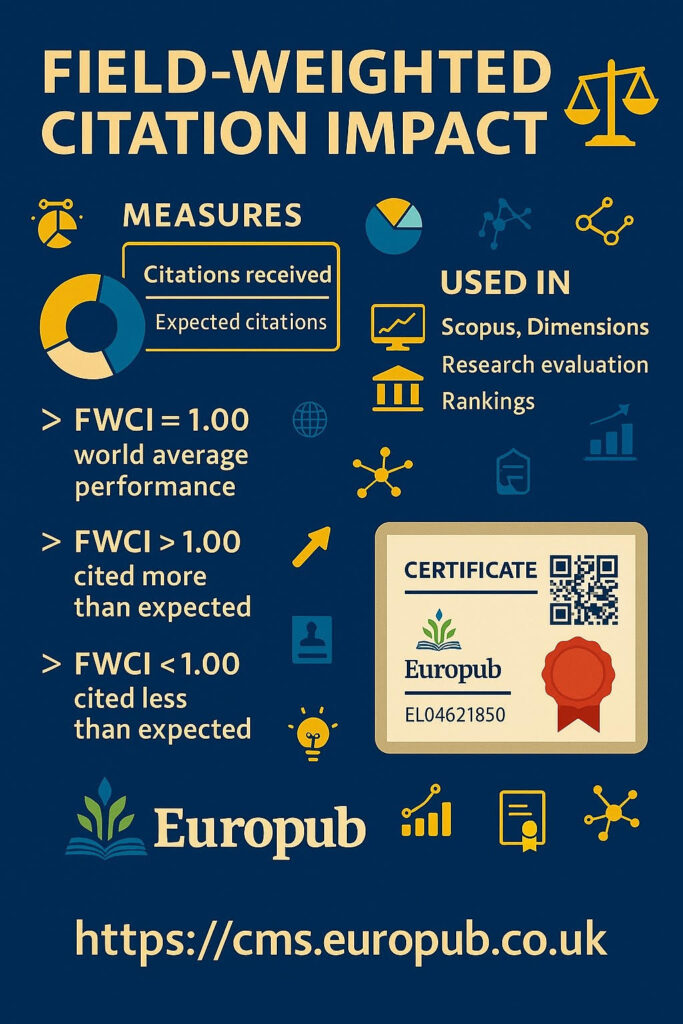
The Field-Weighted Citation Impact (FWCI) measures how well a publication performs in terms of citations compared to similar publications in the same field, year, and document type.
It’s designed to normalize citation performance so that disciplines with different citation behaviors (e.g., physics vs. humanities) can be compared fairly.
 Formula:
Formula:
\text{FWCI} = \frac{\text{Citations received by the paper}}{\text{Expected citations for similar papers}}
 How It Works
How It Works
- FWCI = 1.00 → world average performance
- FWCI > 1.00 → cited more than expected
- FWCI < 1.00 → cited less than expected
 Example:
Example:
If a paper in Agricultural Science has 15 citations, and similar papers average 10,
then FWCI = 15 ÷ 10 = 1.5 (50% higher impact than global average).
 Why FWCI Matters
Why FWCI Matters
Unlike raw citation counts, FWCI adjusts for field differences, allowing fairer comparison across:
- Disciplines with varying citation habits
- Publication years
- Document types (articles, reviews, conference papers)
It helps identify true research influence, not just popularity or output quantity.
 Where FWCI Is Used
Where FWCI Is Used
| Platform | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Scopus / SciVal | FWCI per paper, author, journal, institution |
| Dimensions.ai | Normalized citation ratios |
| Europub Database | Used in Impact Certificates for journals & researchers |
| Times Higher Education (THE) | Ranking indicator for citation impact |
 Advantages of FWCI
Advantages of FWCI
 Normalized across fields
Normalized across fields
 Recognizes quality, not just quantity
Recognizes quality, not just quantity
 Useful for multidisciplinary comparison
Useful for multidisciplinary comparison
 Highlights high-performing authors or institutions
Highlights high-performing authors or institutions
 Aligns with global ranking methodologies
Aligns with global ranking methodologies
 Limitations
Limitations
 Requires a large dataset to calculate accurately
Requires a large dataset to calculate accurately
 Not available for very new publications
Not available for very new publications
 Sensitive to outliers (highly-cited papers can skew averages)
Sensitive to outliers (highly-cited papers can skew averages)
 Does not reflect negative citations or citation context
Does not reflect negative citations or citation context
 FWCI in Practice — Real-World Use
FWCI in Practice — Real-World Use
- Universities use FWCI to benchmark performance in global rankings.
- Funding agencies assess project outcomes using FWCI metrics.
- Journals track editorial impact across subject categories.
- Researchers include FWCI in resumes and grant applications.
 Improving FWCI Ethically
Improving FWCI Ethically
 Publish in high-impact indexed journals (Scopus/WoS)
Publish in high-impact indexed journals (Scopus/WoS)
 Engage in international collaborations
Engage in international collaborations
 Write interdisciplinary studies that appeal to multiple audiences
Write interdisciplinary studies that appeal to multiple audiences
 Promote open access visibility
Promote open access visibility
 Ensure accurate author affiliation and ORCID linking
Ensure accurate author affiliation and ORCID linking
 Related Metrics Comparison
Related Metrics Comparison
| Metric | Measures | Normalized? | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Citation Count | Total number of citations |  No No | Google Scholar, Scopus |
| h-index | Productivity + impact |  No No | Google Scholar, Scopus |
| i10-index | Papers cited ≥10 times |  No No | Google Scholar |
| FWCI | Citations vs. expected for field |  Yes Yes | Scopus, Dimensions |
| RCR (Relative Citation Ratio) | NIH variant of FWCI |  Yes Yes | PubMed, iCite |
 Ethical Use Guidelines
Ethical Use Guidelines
 Do not manipulate citations or self-cite excessively.
Do not manipulate citations or self-cite excessively.
 Avoid comparing FWCI across unrelated disciplines.
Avoid comparing FWCI across unrelated disciplines.
 Use FWCI as a complementary, not the sole, indicator of quality.
Use FWCI as a complementary, not the sole, indicator of quality.
 Report FWCI transparently with data source (e.g., “FWCI = 1.42, Scopus 2024”).
Report FWCI transparently with data source (e.g., “FWCI = 1.42, Scopus 2024”).
 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. What is a good FWCI?
 Above 1.0 indicates performance better than world average.
Above 1.0 indicates performance better than world average.
2.0 means twice the average impact.
Q2. Where can I find my FWCI?
 Scopus (via Author Profile), SciVal, or Europub Impact Certificates.
Scopus (via Author Profile), SciVal, or Europub Impact Certificates.
Q3. How often is FWCI updated?
 Typically every few months as new citations are indexed.
Typically every few months as new citations are indexed.
Q4. What’s the difference between FWCI and Impact Factor?
 Impact Factor applies to journals, while FWCI applies to individual papers or authors.
Impact Factor applies to journals, while FWCI applies to individual papers or authors.
Q5. Can a single highly-cited paper raise my FWCI a lot?
 Yes, but normalization reduces extreme skew compared to raw counts.
Yes, but normalization reduces extreme skew compared to raw counts.
Q6. Why does FWCI vary by database?
 Each platform uses different citation sources and calculation baselines.
Each platform uses different citation sources and calculation baselines.
Q7. Is FWCI affected by Open Access?
 Yes — OA papers tend to have higher FWCI due to visibility.
Yes — OA papers tend to have higher FWCI due to visibility.
Q8. Does collaboration increase FWCI?
 Generally yes, especially international collaborations.
Generally yes, especially international collaborations.
Q9. Can review papers distort FWCI?
 They can — reviews usually receive more citations than research papers.
They can — reviews usually receive more citations than research papers.
Q10. How does FWCI benefit institutions?
 Helps showcase performance in global rankings and funding evaluations.
Helps showcase performance in global rankings and funding evaluations.
Q11. Is FWCI time-sensitive?
 Yes. Newly published papers may have low FWCI early on.
Yes. Newly published papers may have low FWCI early on.
Q12. What does FWCI = 0.5 mean?
 Your paper is cited half as often as similar papers globally.
Your paper is cited half as often as similar papers globally.
Q13. What does FWCI = 3.0 mean?
 Your paper is cited three times more than expected globally.
Your paper is cited three times more than expected globally.
Q14. How does FWCI handle multidisciplinary papers?
 It averages expected citations across all relevant fields.
It averages expected citations across all relevant fields.
Q15. Can Europub provide FWCI certificates?
 Yes. Europub offers Impact Factor & FWCI Certificates with DOI-based validation
Yes. Europub offers Impact Factor & FWCI Certificates with DOI-based validation
 Useful Resources
Useful Resources
- Scopus FWCI Documentation
- Dimensions Metrics Guide
- NIH iCite Tool
- Europub Certificate Management System
 Summary
Summary
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Metric Name | Field-Weighted Citation Impact (FWCI) |
| Formula | Citations received / Expected citations |
| Benchmark | FWCI = 1.0 (world average) |
| Use Case | Cross-field comparison of research performance |
| Source Databases | Scopus, Dimensions, Europub |
| Applications | Ranking, evaluation, funding, certificates |






